TOGAF and infrastructure architecture
TOGAF stands for The Open Group Architecture Framework. It is an extensive method for establishing (Enterprise) Architectures. TOGAF is one of the few methods not developed by one company (like for instance IAF and DYA that are created by Capgemini and Sogeti respectively).The Open Group consists of a consortium of companies and institutions, developing many standards, including TOGAF.
TOGAF describes three types of architectures:
- Business architecture
- Information Systems architecture, which comprises:
- Data architecture and
- Applications architecture
- Technical architecture
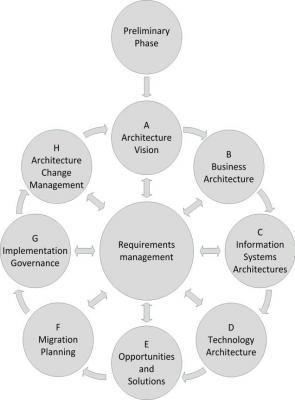
The ADM is the heart of TOGAF. It is an architecture development method.
Figure: TOGAF ADM
The ADM method describes the steps to be taken to come to a complete enterprise architecture or a change to an existing architecture. Every step itself consists of (a large number of) smaller steps.
All steps can be performed sequentially; if in phase H it is concluded that a change of architecture is necessary, the ADM can be re-started from phase A.
It is also possible to use only a part of the ADM (for a particular change or project) or to do all of the ADM, but not all parts in an equally fine grained detail.
TOGAF is an open framework, of which the description can be found on the Internet. TOGAF is also published as a book (700+ pages!) which can be obtained from The Open Group. TOGAF does have a license structure; a fee must be paid if TOGAF is used in a commercial environment. Please check the website of The Open Group for details. For individuals TOGAF can be used under a free license.
TOGAF is an enterprise architecture framework, but it can be useful as a reference in an infrastructure architecture as well. Especially phases D, E and F of the ADM are relevant. Phase D (Technology architecture) is about describing the current and desired architecture and to find the gaps between them. Phase E (Opportunities and Solutions) explains how to create solutions from the desired architecture. And phase F (Migration planning) describes how to determine the projects needed to implement an architecture.
TOGAF also provides examples of architecture principles, stakeholder and requirements management, gap analysis, migration planning techniques and much more, all of them relevant for infrastructure architects.
But be aware that TOGAF is very detailed and complex. It is hard to comprehend and the text can be confusing at some places. Just pick out the parts that are useful in your project.
This entry was posted on Friday 07 June 2013
 Dutch
Dutch