Software Defined Storage (SDS)
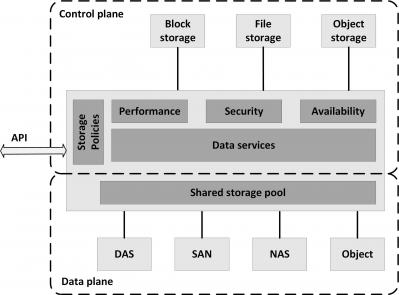
Software Defined Storage (SDS) abstracts data and storage capabilities (the control plane) from the underlying physical storage systems (the data plane). This allows data to be stored in a variety of storage systems while being presented and managed as one storage pool to the servers consuming the storage. The figure below shows the SDS model.
Heterogeneous physical storage devices can be made part of the SDS system. SDS enables the use of standard commodity hardware, where storage is implemented as software running on commodity x86-based servers with direct attached disks. But the physical storage can also be a Storage Area Network, a Network Attached Storage system, or an Object storage system. SDS virtualizes this physical storage into one large shared virtual storage pool. From this storage pool, software provides data services like:
- Deduplication
- Compression
- Caching
- Snapshotting
- Cloning
- Replication
- Tiering
SDS provides servers with virtualized data storage pools with the required performance, availability and security, delivered as block, file, or object storage, based on policies. As an example, a newly deployed database server can invoke an SDS policy that mounts storage configured to have its data striped across a number of disks, creates a daily snapshot, and has data stored on tier 1 disks.
APIs can be used to provision storage pools and set the availability, security and performance levels of the virtualized storage. In addition, using APIs, storage consumers can monitor and manage their own storage consumption.
This entry was posted on Friday 09 September 2016
 Dutch
Dutch