Software Defined Data Center - SDDC
A software-defined datacenter (SDDC) – a term coined by VMware, also known as a Virtual Data Center (VDC), is an architecture in which all infrastructure resources – compute, storage and networking – are virtualized and configured using software APIs.
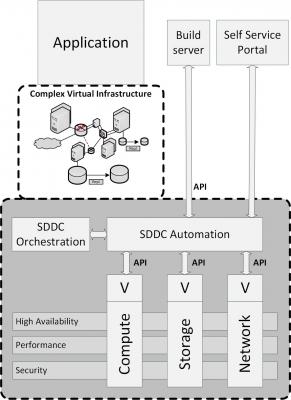
As shown in the figure above, an SDDC is an extension on an enterprise infrastructure, where all resources are virtualized and managed by the SDDC automation and orchestration software.
An SDDC is characterized by automation, orchestration, and abstraction of resources into software and code. By nature, code is more reliable than humans, which means that compared to a traditional datacenter, the SDDC is more secure and more agile. Changes are managed by an automated workflow, where an orchestrated change leads to automated changes in each resource.
An SDDC is the basis for cloud computing. It enables developers, DevOps teams and systems managers to create and deploy new infrastructures using either a self-service portal or automatically by a build server using APIs. It allows the user to select the desired infrastructure components, their sizing to meet performance demands and their required availability, and automatically configures the SDDC components to deliver a secured infrastructure implementation. The SDDC software also provides tools for costing, logging, reporting, scaling (up and down), and decommissioning of the infrastructure resources.
Examples of SDDC automation and orchestration products are OpenStack’s Horizon, IBM Cloud Orchestrator, and VMware vRealize.
An SDDC is not the solution for all problems – there are many applications that need a much more custom-designed infrastructure than the standard building blocks SDDC provides. Examples are SAP HANA, High performance databases, OLTP, High secure bank or stock trade transaction systems, and SCADA systems.
This entry was posted on Thursday 30 April 2015
 Dutch
Dutch